lenvanzanten
Members-
Posts
12 -
Joined
-
Last visited
Everything posted by lenvanzanten
-
Proving einstein wrong in 2 simple steps
lenvanzanten replied to phillip1882's topic in Physics and Mathematics
In reply to Janus and Qfwfq: here is some reasoning in plain terms to consider. We know that the light of stars refracted by our atmosphere places the star at a slightly different location from where it really is. This is for stars that appear close to the horizon, while those appearing directly above us at midnight for example their light passes in by the normal with no refraction. If therefore this is true for all stars by any atmosphere why not so by the Sun? The best time to view the light of a star grazing the Sun would be at midday when it would come to by the normal into our atmosphere, any other time of the day would make that star appear somewhat out of location by its angle into our own atmosphere - - to as we might say; - add to the dislocation. Then for the arberration of the light, we must take in account the high temperature of the media surrounding the Sun in which refraction is minimized. And the great distance, which for the smallest of arc’s causes to enlarge the appearant relocation of the star. Adding this together our own possible dislocation – why should we not behold pretty well most of the visible wavelengths? When we consider the red sky in the evening here on Earth to view mostly the longer lengths, we must consider how we from our view point are in the middle and at the bottom of the refractive index. And so I deem it fair to consider these and more such phenomena before in this case we scrap light’s refraction grazing the Sun as of no relevance -
Proving einstein wrong in 2 simple steps
lenvanzanten replied to phillip1882's topic in Physics and Mathematics
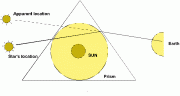
The cause for the apparent location of a star verses that of its actual location is due to the refraction of its light as the same grazes the sun through its atmosphere. (Illustration) The same is true for the Sun appearing above the horizon when in fact it is below the horizon. To date no real evidence has been furnished that light for its movement is susceptible to gravitational forces. Gravity has shown to act upon all atomic substance, but no evidence to act upon wave formations. The theory of light not escaping from a so called black hole as speculation cannot be construed as evidence, while the refraction of light as illustrated is abundantly evident. As far as a delay in the reduction of the velocity of light grazing the sun, however difficult such is to measure, is due to the density of the plasma (atmosphere surrounding the sun) verses the density of space. Opting “newtonphysics.on.ca/ECLIPSE/Eclipse.html” likewise shows relavistic errors The irony of it is – Einstein’s prediction that light would bend in passing near the Sun, is hardly a prediction, but a known fact as it does so by any sphere or prism. One need not predict known common occurances, but to replace the known factual refraction of light into an assumption of gravitational deflection is at best mis-appropiation. A quotation from the listed website Quote: So now we find that the legend of Albert Einstein as the world's greatest scientist was based on the Mathematical Magic of Trimming and Cooking of the eclipse data to present the illusion that Einstein's general relativity theory was correct in order to prevent Cambridge University from being disgraced because one of its distinguished members [Eddington] was close to being declared a "conscientious objector". -
Proving einstein wrong in 2 simple steps
lenvanzanten replied to phillip1882's topic in Physics and Mathematics
-
Proving einstein wrong in 2 simple steps
lenvanzanten replied to phillip1882's topic in Physics and Mathematics
Simple logic Look up online dictionary of light through a prism, it states that: "Light refracts due to the different velocities of light" How then do we say light has a constant velocity everywhere? And does not the prism concludes light to vary in velocity by passing through densities, as it did by our atmosphere in the Michelson Morley experiment? Who now will tell us that these reduction in velocities are real or apperent, and why? -
Proving einstein wrong in 2 simple steps
lenvanzanten replied to phillip1882's topic in Physics and Mathematics
Philip is correct, Michelson and Morley proved light riding dependent on the media, Therefore light from a star coming from behind the direction of Earth's movement travels with the velocity of the speed of light plus the velocity of the Earth, relevant to space as a fixed reference. Its very simple light moving at c as it entered upon our solar system, became dependant on it and its movement wherefore Michelson and Morly read the two opposing velocities the same. The experiment proved conclusively that; Relevant to space lights velocity can be greater as well as less to the constant of the velocity of light. Does not this make good sense? -
I have heard enough, the erro of man is held viable while truth and reality are considered strange. I therefore am quiting the forum. This however I am sure of; that current foundations of science will be replaced by a new foundation, one that inhibits truth with reality. I will mention a new law of gravity which does not require reference, it being indisputable in itself. ; "The gravitational force upon a mass in uniform circular motion is; its weight times the value of g at the radius thereof."
-
QUOTE: Next g-force, or “gees”, is not a force, but a unit of perceived acceleration, such that 1 g is the acceleration experienced by an accelerometer on the Earth’s surface. Sorry CraigD I did not mean to be rough but a bit return of your own medicine, Tell me then on the above g is very much a force standing still on the ground, as much as it is under acceleration. The value is used for both and even when no gravitational direction is present such as a car making a turn in the horizontal plane. It applies since the ever present g is by and in the inertia of all substance, (Therein by the way lies also the secret to how and what gravity is, but a lenghty subject)
-
Much thanks Modest for your reply, that makes good sense. I did not really think the calcs were wrong, but why they did so. In my book (as also in the textbooks) however whatever one makes of it, the term acceleration should only be used where there is in fact and indeed an increase in velocity, a change in speed not a change in direction when speed remains constant. And don't get me wrong I know all the arguments given.
-
I put this on to see what responds there would be, but you seem to be more confused than the persons constructing the calculators.
-
It looks like the experts in their online calculations have yet to figure out how to compute gravity and/or centrifugal force. Let us take a 3000 lb rocket at 200 miles up traveling 18.000 mph Example 1: 3000-lb x 26,400-ft/sec2 : 22,176,000-ft/r = 94,286-lb/cg Then that same rocket at the equator. Example 2: 3000-lb x 1521-ft/sec2 : 20,929,920-ft/r = 331.6 lb/cg The online calcs specify 2930.4 lb for example 1 and 10.3 lb for example 2. On the ground we specify G/force at 3000 + 331.6 to 3331.6 lb, and 200 miles up at 18.000 mph at 94,286 lb. If then we simply lift that rocket straight up to 200 miles above earth to travel with the same speed as the earth’s rotation (1000 mph) what would be its weight in G force? In order to be correct we must determine what the figure of G is 4200 miles from earth’s center. Assuming the rocket is balanced in orbit, and assuming g at about 90% down from 32.14 to 31.43, the 94286 : 31.43 = 3000 lb. The new weight of the rocket 200 ft up therefore is 2933.7 lb. Then: 2933.7 lb x 1521 ft/sq : 22176000 ft/r = 306 lb centrifugal force, this added to its basic weight, G/force comes to 3239.7 lb of G/force on the rocket with only 306 lb of centrifugal holding it up, which by law of equal action to reaction cannot possibly stay up there. The scientists with their online calcs are however telling us that it will stay up there by no more than 2930.4 lb of G/force, as g and c (for centrifugal) must be equal. But how can they possibly come up with a c and g of less than its own weight at a velocity 18 times faster than sitting still on earth and/or 200 miles up? Why accelerate it 18000 mph? Whatever happen to the square of the force in linear motion? Is 18000 mph so minute in force, while at a mere 60 mph a car into a brick wall will be smashed? These fellows rewrote the law as follows: "The gravitational acceleration of a mass in uniform circular motion is proportional to the square of its speed and inversely to the radius of its path, and once again inversely to its inertial gravity." For that is how they came to their eroneous figures. The link to the calc is (on line) (calctool) The above weight, speed, and radius are for example, actual velocity of space shuttle 17,532 mph
-
"Modest" is correct he knows his stuff.
-
Yes it is called Centrifugal force. (Newton's law)